Programming serves as the foundation for virtually every digital device and application used today, from smartphones to websites to artificial intelligence systems. Understanding programming fundamentals opens doors to problem-solving skills, creative expression, and numerous career opportunities in our increasingly digital world. Learning to code might seem daunting at first, but breaking it down into manageable steps makes the journey both accessible and rewarding.
This guide walks beginners through the essential building blocks of programming, starting with core concepts and progressing to practical applications. Readers will discover how to choose their first programming language, set up a proper development environment, and understand fundamental concepts like variables and control structures. The journey extends beyond basic syntax to explore real-world applications and pathways for continued growth.
Whether someone aspires to build mobile applications, develop websites, or simply understand how technology works, mastering programming basics provides the foundation for countless possibilities. The skills developed through coding extend far beyond writing instructions for computers, fostering logical thinking and systematic problem-solving approaches that prove valuable in many aspects of life.
What Is Programming?
Programming involves writing step-by-step instructions that computers can understand and execute to perform specific tasks. These instructions form the foundation of modern technology, enabling everything from mobile applications to artificial intelligence systems.
How Computers Understand Instructions
Computers operate using binary code, which consists of ones and zeros that represent electrical states. Programming languages serve as intermediaries between human thought and machine execution.
High-level programming languages like Python, Java, and JavaScript allow developers to write code using English-like syntax. These languages get translated into machine code through compilers or interpreters.
The translation process converts human-readable instructions into binary format. For example, when a programmer writes print(“Hello World”) in Python, the interpreter converts this command into machine code that tells the processor to display text on screen.
Modern processors execute billions of these binary instructions per second. Each instruction performs basic operations like moving data, performing calculations, or making decisions based on conditions.
The Role of Programming in Technology
Programming drives virtually every digital system we encounter daily. Software development creates applications ranging from simple calculators to complex operating systems that manage entire computer networks.
Artificial intelligence relies heavily on programming to process vast amounts of data and make intelligent decisions. Machine learning algorithms use programmed instructions to recognise patterns and improve performance over time.
Data analysis and data science depend on programming languages like Python and R to extract insights from large datasets. These tools help businesses make informed decisions and researchers discover new knowledge.
Automation through programming eliminates repetitive tasks across industries. From manufacturing robots to automated trading systems, programmed instructions enable machines to work independently and efficiently.
Web development, mobile applications, and embedded systems all require programming expertise to function properly.
Fundamental Programming Concepts
All programming languages share core concepts that beginners must understand. Variables store data values, whilst functions organise code into reusable blocks that perform specific tasks.
Control structures dictate how programmes execute:
- Conditional statements (if/else) make decisions based on data
- Loops repeat actions until conditions are met
- Functions break complex problems into manageable pieces
Data types define what kind of information programmes can process:
|
Data Type |
Example | Purpose |
|
Integer |
42 |
Whole numbers |
|
String |
“Hello” |
Text data |
|
Boolean |
True/False |
Logical values |
| Array | [1,2,3] |
Multiple values |
Algorithms provide step-by-step solutions to problems. These logical sequences form the backbone of effective programming, whether creating simple calculations or complex software development projects.
Understanding these concepts enables programmers to solve real-world problems systematically.
Choosing Your First Programming Language
Selecting the right programming language depends on career goals, project interests, and learning preferences. The most beginner-friendly options include Python and JavaScript due to their readable syntax, whilst languages like Java and Swift offer specific advantages for mobile development and enterprise applications.
Popular Choices for Beginners

Python stands out as the top recommendation for new programmers. Its clean syntax resembles natural English, making it easier to understand programming concepts without complex rules.
Python excels in data science, automation, and web development. Major companies use Python for artificial intelligence and machine learning projects.
JavaScript ranks as the second most popular choice for beginners. It powers all modern websites and enables immediate visual results in web browsers.
New programmers can see their JavaScript code working instantly without installing additional software. This immediate feedback helps maintain motivation during the learning process.
Scratch provides an excellent starting point for absolute beginners, especially younger learners. This visual programming language uses drag-and-drop blocks instead of text-based code.
Ruby offers another beginner-friendly option with elegant syntax. The language emphasises programmer happiness and productivity through its readable structure.
|
Language |
Best For | Difficulty | Job Market |
|
Python |
Data science, automation | Easy | High |
|
JavaScript |
Web development | Easy | Very High |
| Java | Enterprise, Android | Medium |
High |
| Swift | iOS app development | Medium |
Medium |
| C++ | Game development, systems | Hard |
Medium |
Python requires minimal setup and allows beginners to focus on learning programming logic rather than syntax complexity. Its extensive libraries support various applications from web development to scientific computing.
JavaScript enables immediate practice through web browsers. Beginners can create interactive websites and see results instantly, which reinforces learning.
Java offers more structure but requires understanding object-oriented programming concepts early. The language powers Android app development and enterprise systems.
Swift provides the pathway to iOS app development but limits programmers to Apple’s ecosystem. The language offers modern syntax whilst maintaining performance.
C++ demands deeper understanding of computer memory and system operations. Game developers often choose C++ for performance-critical applications and Unity game engine programming.
Aligning Language Choice With Career Goals
Web development careers require JavaScript knowledge as a fundamental skill. Front-end developers create user interfaces, whilst full-stack developers combine JavaScript with server-side languages like Python.
Modern web development frameworks such as React and Angular rely heavily on JavaScript. These tools remain essential for professional web development roles.
Data science professionals primarily use Python due to its powerful libraries and statistical capabilities. Companies seeking data analysts and machine learning engineers favour Python experience.
Game development paths typically involve C++ for high-performance games or C# for Unity projects. Mobile game developers often choose these languages for cross-platform compatibility.
App development splits between Swift for iOS applications and Java or Kotlin for Android platforms. Cross-platform solutions like React Native use JavaScript to target both systems simultaneously.
Enterprise software development heavily favours Java due to its stability and scalability. Large organisations rely on Java for backend systems and business applications.
Beginners should research job advertisements in their target location to understand local demand. Different regions may favour specific programming languages based on dominant industries and company preferences.
Setting Up Your Programming Environment

A proper programming environment requires three essential components: a code editor or integrated development environment for writing code, the necessary tools and compilers to run programs, and a version control system to track changes and collaborate with others.
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) and Text Editors
An integrated development environment (IDE) combines multiple programming tools into a single application. IDEs typically include a text editor, debugger, compiler, and project management features all in one interface.
Visual Studio Code stands out as the most popular choice for beginners. This free text editor offers extensive customisation through extensions and supports virtually every programming language. It provides syntax highlighting, auto-completion, and integrated terminal access.
Popular IDE Options:
- IntelliJ IDEA: Excellent for Java development with advanced debugging features
- PyCharm: Specifically designed for Python with intelligent code assistance
- Sublime Text: Lightweight and fast with minimal resource usage
- Atom: Open-source with strong community support
IDEs often consume more system resources than simple text editors. Beginners should start with Visual Studio Code due to its balance of features and simplicity.
The choice between an IDE and text editor depends on project complexity and personal preference. Simple text editors work well for learning basic concepts, whilst IDEs become valuable for larger projects requiring debugging and project management capabilities.
Installing Tools and Compilers
Programming languages require specific tools to convert human-readable code into executable programs. Compilers translate code into machine language, whilst interpreters execute code directly without pre-compilation.
Installation Requirements by Language:
- Python: Download from python.org, includes interpreter and package manager (pip)
- Java: Install Java Development Kit (JDK) for compiling and running programs
- JavaScript: No installation needed for web development, runs in browsers
- C++: Requires compiler like GCC (Linux/Mac) or Visual Studio (Windows)
Most modern operating systems include package managers to simplify tool installation. Windows users can utilise Chocolatey, macOS users have Homebrew, and Linux distributions include built-in package managers like apt or yum.
Node.js deserves special mention for JavaScript developers. It enables server-side JavaScript development and includes npm (Node Package Manager) for installing libraries and frameworks.
Always verify installations by running version commands in the console. For example, python –version confirms Python installation success.
Version Control Systems
Git represents the industry standard for version control, tracking changes in code over time and enabling collaboration between multiple developers. It creates snapshots of projects at different points, allowing developers to revert changes or merge contributions from team members.
GitHub provides cloud-based Git repository hosting with additional collaboration features. It offers free accounts for public repositories and serves as a portfolio platform for showcasing programming projects to potential employers.
Basic Git Commands:
- git init: Initialise new repository
- git add: Stage changes for commit
- git commit: Save changes with descriptive message
- git push: Upload changes to remote repository
Setting up Git requires configuring username and email address globally on the system. These details appear in commit history and identify the author of code changes.
Repository hosting alternatives include GitLab and Bitbucket, though GitHub maintains the largest developer community. Learning Git early in the programming journey prevents future headaches when managing complex projects or collaborating with others.
Learning Core Programming Concepts
Understanding variables, loops, and functions forms the foundation of programming knowledge. These concepts allow developers to store data, control program flow, and organise code into reusable components.
Variables and Data Types
Variables serve as containers that store information during program execution. A programmer assigns values to variables using a name and can change these values throughout the program’s lifetime.
Basic data types include:
- Integers: Whole numbers like 42 or -15
- Strings: Text enclosed in quotes such as “Hello World”
- Booleans: True or false values for logical operations
- Floats: Decimal numbers like 3.14 or 2.5
Different programming languages handle variable declaration differently. Python allows dynamic typing where age = 25 creates an integer variable automatically. JavaScript uses keywords like let or const to declare variables.
Each data type supports specific operations. Integers and floats work with arithmetic operators (+, -, *, /). Strings can be concatenated using the + operator in many languages. Boolean values enable conditional logic through comparison operators.
Understanding data types prevents common errors. Adding a string to an integer may cause unexpected results or program crashes depending on the language used.
Loops and Conditional Statements
Conditional statements control program execution based on specific conditions. The if-else statement executes different code blocks depending on whether a condition evaluates to true or false.
if temperature > 30:
print(“It’s hot today”)
else:
print(“Pleasant weather”)
Switch statements handle multiple conditions more efficiently than nested if-else structures. They compare a variable against several possible values and execute the matching code block.
Loops repeat code blocks multiple times, reducing redundancy. The for loop runs a predetermined number of times, making it ideal for processing arrays or counting operations.
While loops continue executing whilst a condition remains true. They’re useful when the number of iterations isn’t known beforehand.
Do-while loops execute code at least once before checking the condition. This ensures the code block runs even if the initial condition is false.
Nested loops place one loop inside another, enabling complex data processing like working with two-dimensional arrays or creating patterns.
Functions and Modularity
Functions encapsulate specific tasks into reusable code blocks. They accept input parameters, process data, and optionally return results to the calling code.
Function definition requires a name, parameter list, and code body. Python uses def function_name(parameters): whilst JavaScript uses function functionName(parameters) {}.
Parameters allow functions to work with different data each time they’re called. A function calculating area might accept length and width as parameters.
Return values enable functions to send results back to the caller. This makes functions versatile tools for calculations and data processing.
Functions promote modularity by breaking large problems into smaller, manageable pieces. Each function handles one specific responsibility, making code easier to test and maintain.
Scope determines where variables can be accessed. Variables declared inside functions typically remain local to that function, preventing conflicts with other parts of the program.
Well-designed functions improve code readability and reduce duplication. They form the building blocks for more complex programming concepts like algorithms and data structures.
Exploring Practical Applications
Programming skills translate directly into creating websites with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, building mobile and desktop applications, developing games through engines like Unity, and automating repetitive tasks through scripting.
Basics of Web Development

Web development forms the foundation of modern digital experiences. HTML structures content, CSS handles styling and layout, whilst JavaScript adds interactivity and dynamic behaviour.
HTML creates the skeleton of web pages using elements like headings, paragraphs, and links. CSS transforms plain HTML into visually appealing designs through colours, fonts, and responsive layouts.
JavaScript brings websites to life. It handles user interactions, form validation, and dynamic content updates without page refreshes.
Modern frameworks simplify development:
- React builds component-based user interfaces
- Vue.js offers progressive framework capabilities
- Node.js enables JavaScript server-side programming
Beginners typically start with static HTML pages, then add CSS styling, followed by JavaScript functionality. This progression builds understanding of how web technologies work together.
Full-stack development combines frontend user interfaces with backend server logic. Popular combinations include React with Node.js or Vue.js with various backend technologies.
Introduction to App and Game Development

Mobile app development targets smartphones and tablets across different platforms. Android app development uses Java or Kotlin, whilst iOS development employs Swift or Objective-C.
Cross-platform frameworks reduce development time:
- React Native uses JavaScript for both iOS and Android
- Flutter employs Dart language for native performance
- Xamarin leverages C# for Microsoft ecosystems
Game development requires understanding of graphics, physics, and user input systems. Unity dominates as a beginner-friendly game engine supporting 2D and 3D projects.
Unity uses C# scripting for game logic, character movement, and user interface elements. It supports multiple platforms including PC, mobile, and gaming consoles.
Game development concepts include sprite animation, collision detection, and state management. Simple projects like puzzle games or platformers teach fundamental programming patterns.
Automation and Scripting
Automation eliminates repetitive manual tasks through programmed scripts. Common applications include file management, data processing, and system administration tasks.
Python excels at automation due to its readable syntax and extensive library ecosystem. Scripts can rename files, process spreadsheets, or download web content automatically.
Web scraping extracts data from websites programmatically. Libraries like BeautifulSoup and Selenium handle different scraping scenarios from static pages to dynamic content.
Task scheduling runs scripts at specific times or intervals. Operating systems provide built-in schedulers whilst cloud platforms offer automated execution environments.
Scripting integrates different software systems. APIs allow programs to communicate, enabling data transfer between applications without manual intervention.
System administration benefits significantly from automation. Scripts can monitor server performance, backup databases, and deploy software updates consistently across multiple machines.
Building Skills Through Practice and Community
Regular practice through coding challenges and active participation in programming communities accelerate skill development more effectively than solo learning. Engaging with open source projects provides real-world experience whilst connecting with other developers creates valuable learning opportunities.

Coding Challenges and Learning Platforms
Coding challenges provide structured practice that strengthens problem-solving abilities and programming fundamentals. Platforms like LeetCode and HackerRank offer thousands of problems ranging from basic algorithms to complex data structures.
These platforms typically organise challenges by difficulty level and topic. Beginners should start with easy problems focusing on arrays, strings, and basic loops before progressing to medium-difficulty challenges.
FreeCodeCamp combines coding challenges with project-based learning. Students complete interactive lessons followed by real-world projects like building responsive websites or data visualisation tools.
Codecademy offers guided practice with immediate feedback. Their interactive coding environment allows students to write code directly in the browser whilst learning syntax and concepts.
W3Schools provides practical examples and exercises for web development technologies. Each tutorial includes “Try it Yourself” sections where students can experiment with code modifications.
Regular practice sessions of 30-60 minutes daily yield better results than lengthy weekend sessions. Consistent engagement helps reinforce concepts and builds programming intuition over time.
Contributing to Open Source
Open source contributions provide exposure to real-world codebases and professional development practices. GitHub hosts millions of repositories where beginners can find projects matching their skill level and interests.
Start by exploring projects with “good first issue” or “beginner-friendly” labels. These issues typically involve documentation updates, bug fixes, or small feature additions that don’t require deep codebase knowledge.
Reading existing code teaches valuable lessons about code organisation, commenting practices, and problem-solving approaches. Contributors learn to navigate large projects and understand how different components interact.
The contribution process involves forking repositories, creating branches, making changes, and submitting pull requests. This workflow mirrors professional software development practices used in most technology companies.
Many open source maintainers provide feedback on contributions, offering personalised code reviews that accelerate learning. This mentorship aspect proves invaluable for skill development and best practice adoption.
Connecting With the Programming Community
Programming communities offer support, knowledge sharing, and networking opportunities that enhance the learning experience. Stack Overflow serves as the primary question-and-answer platform where developers seek help with specific coding problems.
Reddit hosts numerous programming communities like r/learnprogramming and r/programming where beginners can ask questions, share projects, and receive feedback from experienced developers.
Local meetups and online forums provide opportunities to connect with nearby developers. These gatherings often feature presentations on new technologies, coding workshops, and networking sessions.
Discord servers and Slack communities offer real-time chat environments where programmers discuss projects, share resources, and collaborate on solutions. Many communities maintain channels dedicated to specific programming languages or technologies.
Engaging with communities requires active participation rather than passive observation. Answering questions, sharing helpful resources, and providing code reviews contributes to community growth whilst reinforcing personal knowledge through teaching others.
Opportunities and Career Pathways
Programming skills unlock access to high-paying positions across multiple industries, from traditional software companies to emerging fields like artificial intelligence and data science. The demand for skilled programmers continues to grow,creating diverse employment opportunities for beginners willing to learn.
Careers in Software and Web Development
Software developers build applications for desktop computers, mobile devices, and enterprise systems. Entry-level positions typically start at £25,000-35,000 annually, with senior roles reaching £60,000-80,000.
Web developers specialise in creating websites and web applications. Front-end developers focus on user interfaces using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Back-end developers handle server-side programming with languages like Python, Java, or PHP.
Mobile app development represents a growing sector. iOS developers use Swift, whilst Android developers work with Java or Kotlin. Many companies seek full-stack developers who can handle both front-end and back-end responsibilities.
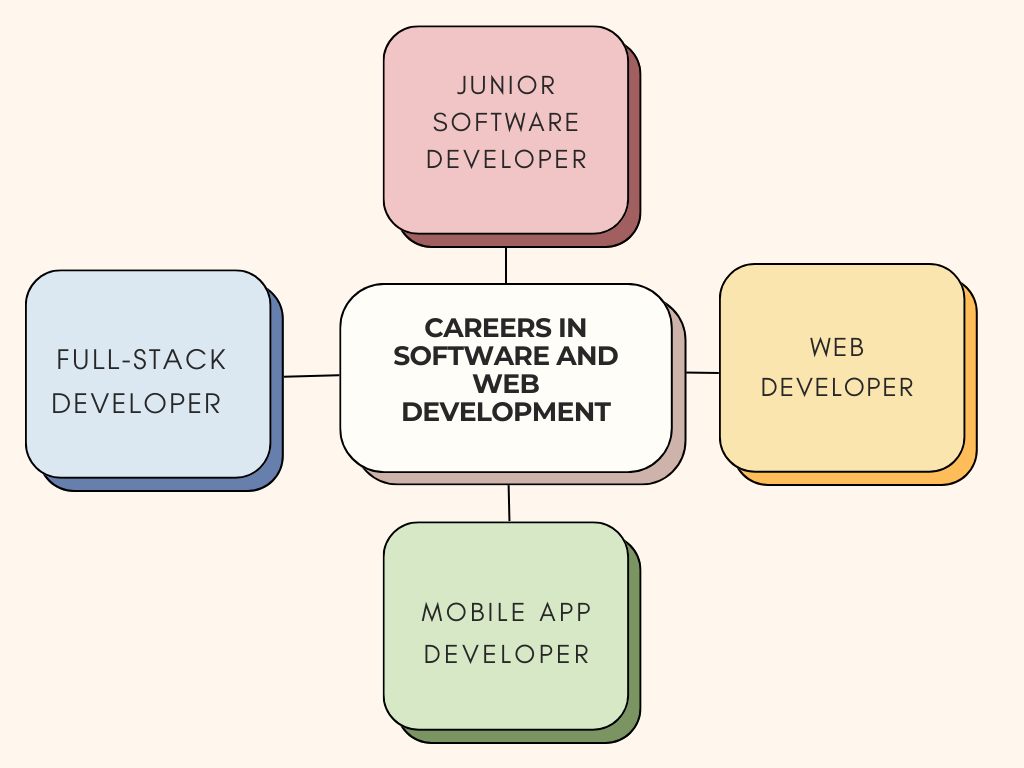
Key development roles include:
- Junior Software Developer (£22,000-30,000)
- Web Developer (£20,000-28,000)
- Mobile App Developer (£25,000-35,000)
- Full-Stack Developer (£30,000-45,000)
Many positions offer remote work options and flexible schedules. Startups often provide equity compensation alongside salary packages.
Programming in Emerging Fields
Data science combines programming with statistical analysis to extract insights from large datasets. Data scientists use Python and R to build predictive models and create visualisations. Entry-level positions start around £30,000-40,000.
Machine learning engineers develop AI systems that learn from data. They work with frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch to create recommendation systems, image recognition software, and natural language processing applications.
Artificial intelligence roles span multiple industries including healthcare, finance, and autonomous vehicles. AI specialists command some of the highest salaries in technology, often exceeding £50,000 for junior positions.
Cybersecurity analysts protect systems from digital threats using programming skills to develop security tools and analyse vulnerabilities. The field offers strong job security due to increasing cyber threats.
Emerging field salary ranges:
- Data Scientist: £35,000-70,000
- Machine Learning Engineer: £40,000-80,000
- AI Specialist: £45,000-90,000
- Cybersecurity Analyst: £30,000-60,000
Maximising Employability With Programming Skills
Building a portfolio demonstrates practical abilities to potential employers. GitHub repositories showcase coding projects and collaborative skills. Contributing to open-source projects provides real-world experience.
Networking accelerates career progression through tech meetups, conferences, and online communities. LinkedIn profiles highlighting programming skills attract recruiter attention and job opportunities.
Continuous learning keeps skills current with evolving technologies. Online courses, bootcamps, and certifications supplement formal education. Many professionals learn new languages and frameworks throughout their careers.
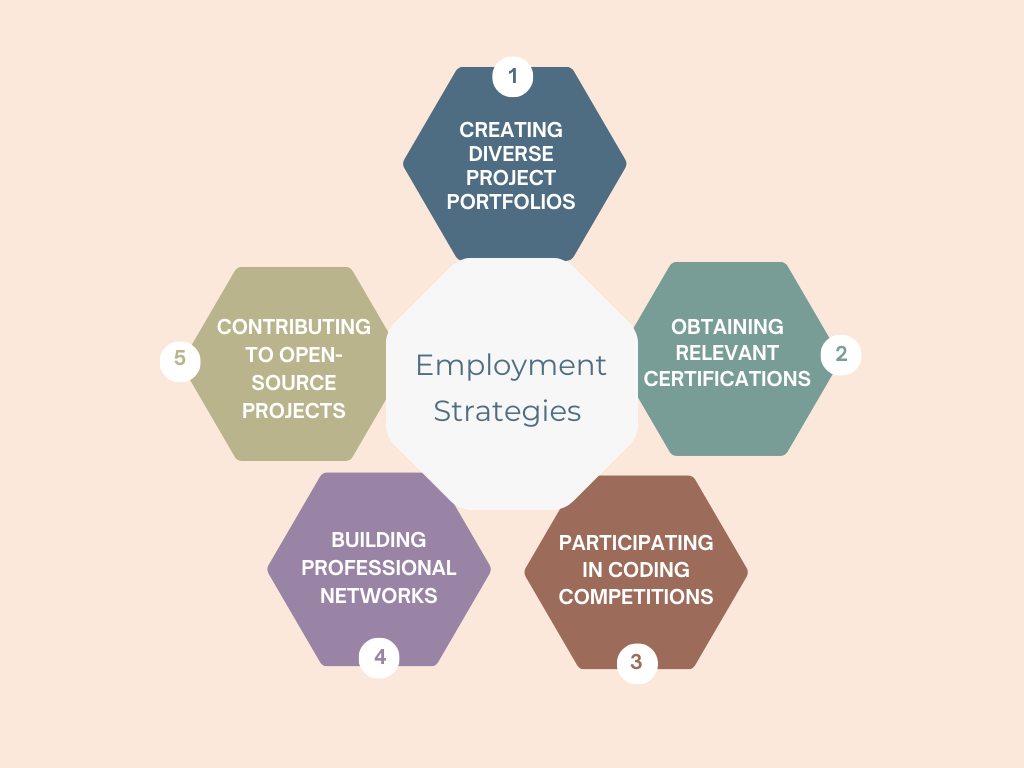
Employment strategies include:
- Creating diverse project portfolios
- Obtaining relevant certifications
- Participating in coding competitions
- Building professional networks
- Contributing to open-source projects
Freelancing offers flexibility for experienced programmers. Platforms like Upwork and Freelancer connect developers with clients seeking custom solutions. Rates vary from £15-100 per hour based on expertise.
Many companies value problem-solving abilities over specific qualifications. Bootcamp graduates often secure positions alongside computer science degree holders when they demonstrate practical skills through projects and portfolios.